
Greutăți și măsuri
| Lungime | de la 18 la 22 cm |
|---|
Date biologice
| Durata de viață | de la 20 la 40 ani |
|---|
Starea de conservare
| Amenințat |
Descrierea animalului
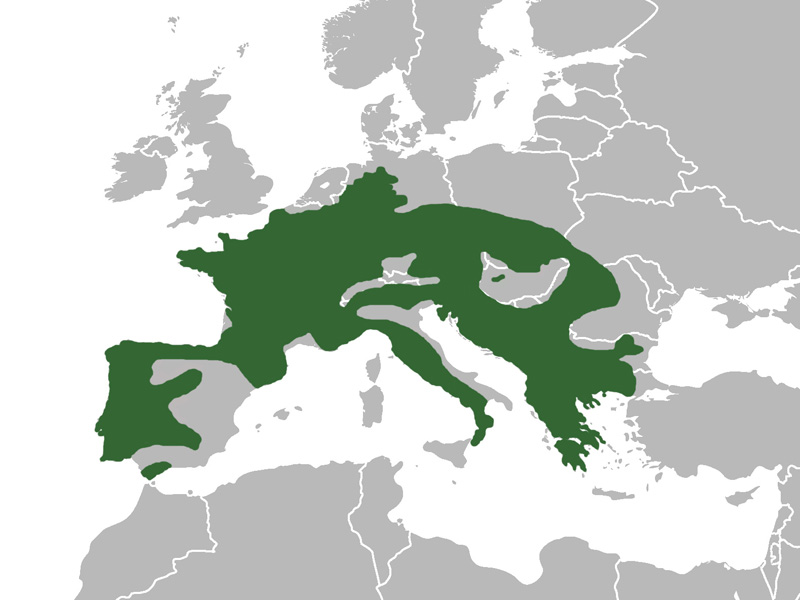
The Fire Salamander (Salamandra salamandra) is a striking species of amphibian, renowned for its vivid coloration and unique ecological role within its habitat. This species is primarily distributed across various parts of Europe, with its presence spanning from the Iberian Peninsula in the west through to the Balkans and parts of the Middle East in the east. The Fire Salamander's habitat is largely confined to temperate forests, where it prefers moist environments such as deciduous forests, woodlands, and areas near streams and rivers.One of the most distinctive features of the Fire Salamander is its vibrant coloration. The base color of its skin is typically a deep, glossy black, which serves as a backdrop for bright yellow to orange markings. These markings are not just for show; they serve as a warning to predators about the salamander's toxic secretions. The patterns and the intensity of the colors can vary greatly among individuals, making each Fire Salamander uniquely beautiful.
The Fire Salamander has a robust and somewhat elongated body, with a broad, flat head and large, bulging eyes. It possesses short limbs that are well-adapted for its life on the forest floor. Adult Fire Salamanders typically range in size from 15 to 25 centimeters in length, though size can vary based on environmental conditions and subspecies variations.
This amphibian leads a primarily nocturnal lifestyle, seeking refuge under logs, stones, and leaf litter during the day and emerging at night to hunt. Its diet is carnivorous, consisting mainly of insects, worms, and other small invertebrates. The Fire Salamander employs a sit-and-wait strategy for hunting, remaining motionless until prey comes within striking distance.
Reproduction in Fire Salamanders is particularly fascinating. Depending on the subspecies and the environmental conditions, they can reproduce in two different ways. Some populations are ovoviviparous, where the female retains the fertilized eggs inside her body until they hatch, giving birth to fully formed, live young. Others lay eggs in water, which then hatch into aquatic larvae. These larvae undergo metamorphosis, transforming into terrestrial adults.
One of the most remarkable aspects of the Fire Salamander is its defense mechanism. When threatened, it is capable of secreting a potent toxin from glands located on its back and behind its head. This neurotoxin can cause irritation and harm to potential predators, and in some cases, can be lethal if ingested.
Despite their beauty and ecological importance, Fire Salamanders face several threats, including habitat destruction, pollution, and the spread of diseases such as the chytrid fungus, which has decimated amphibian populations worldwide. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the survival of this fascinating species, highlighting the need for habitat protection, pollution control, and disease management.
In summary, the Fire Salamander is a captivating and important amphibian species, with its vivid colors, interesting behaviors, and ecological role. Its presence in European forests adds to the biodiversity and complexity of these ecosystems, underscoring the importance of conservation efforts to protect these remarkable creatures and their habitats.
Harta răspândirii
Animale similare
Fotografii noi cu animale
Top 10 animale
- Dolphin gull (Leucophaeus scoresbii)
- Diana monkey (Cercopithecus diana)
- Moustached guenon (Cercopithecus cephus)
- Stone loach (Barbatula barbatula)
- Greek tortoise (Testudo graeca)
- Galápagos tortoise (Geochelone nigra complex)
- Japanese macaque (Macaca fuscata)
- Russian tortoise (Testudo horsfieldii)
- Common flying dragon (Draco volans)
- Galápagos penguin (Spheniscus mendiculus)


